 Back to all articles
Back to all articles
Everyone is buzzing with news about the latest AI breakthroughs, and we at Setronica believe in moving beyond the headlines to explore its practical applications.
As we deal with the human impact on our planet, it’s high time we asked: Can AI help us take care of it?
And indeed, AI is proving to be a powerful tool in addressing the growing waste problem. As landfills fill up and plastic pollutes the oceans, we urgently need better recycling methods. This is where AI comes in, offering real solutions today, not just promises for the future.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI is making recycling more accurate and efficient through better sorting and constant monitoring.
Let’s not waste any more time and get down to it.
AI waste recognition is like teaching a computer to see and understand different types of trash. But in this case, AI uses computer vision and machine learning algorithms to figure out what kind of waste an item is. Here’s how it works:
Just like how we learn to recognize things by seeing them many times, AI systems learn from lots of pictures. They’re shown thousands of images of different waste items – plastic bottles, paper, food scraps, and more. Each picture is labeled to tell the AI what it’s looking at. Over time, the AI gets really good at spotting the differences.
At a recycling facility, AI-powered waste recognition systems operate continuously, processing thousands of items per hour. As waste materials move through the facility on high-speed conveyor belts, the AI follows these steps:
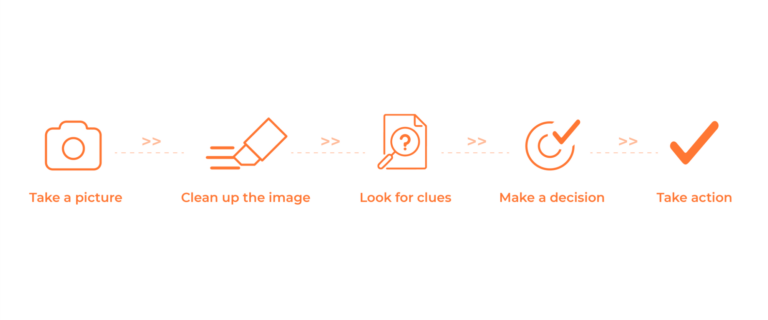
Modern AI waste recognition systems have evolved to perform complex tasks that go far beyond simple sorting:
Smart waste management systems are like high-tech puzzles that fit together to make recycling better. Here are the main components:
All these sensors are constantly collecting data. It’s like they’re all talking to each other and to a central computer system. This creates a treasure trove of information about the waste being processed.
Let’s look at some types of sensors and what they do:
Imagine a recycling center where machines can pick up, sort, and separate different types of trash quickly and accurately. That’s exactly what AI-powered sorting mechanisms do.
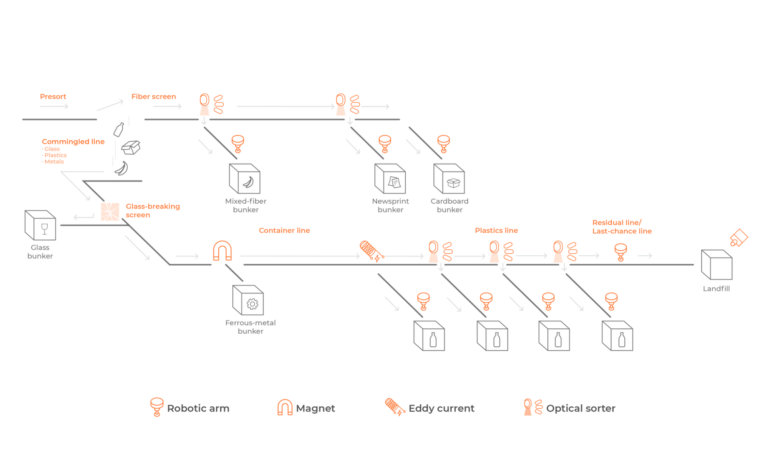
Data analytics and reporting tools take in all the data from sensors and sorting machines, and turning it into useful information.
These systems help recycling teams understand what’s happening right now and make better decisions. They can show things like what types of waste are most common and how well the recycling process is working.
But these systems don’t just look at the present – they can also predict what might happen in the future. Using AI algorithms, they can guess how much waste might be generated during busy times or when machines might need fixing. This helps recycling facilities plan ahead and work more efficiently.
AI waste management systems prove their worth daily across multiple sectors. Here are a few examples that show operational gains and environmental benefits.
Recycling is becoming smarter and more convenient for everyone. Smart bins are popping up in homes, offices, and public spaces. These high-tech containers use AI to identify what you’re throwing away.
Some have multiple compartments and automatically open the right one for your item. Others use voice commands, so you can ask, “Where does this go?” and get an instant answer. These bins take the guesswork out of recycling, ensuring items end up in the right place.
Mobile apps use image recognition to identify materials and provide specific local recycling instructions.
These smart solutions are doing more than just making recycling easier – they’re educating users too. Both bins and apps often provide interesting facts about recycling and the environmental impact of proper waste management. This ongoing education helps build better recycling habits over time.
With open dumps and various forms of landfills still dominating the waste management, there’s significant room for improvement. AI-powered solutions are stepping in to help businesses navigate this complex waste management landscape more effectively.
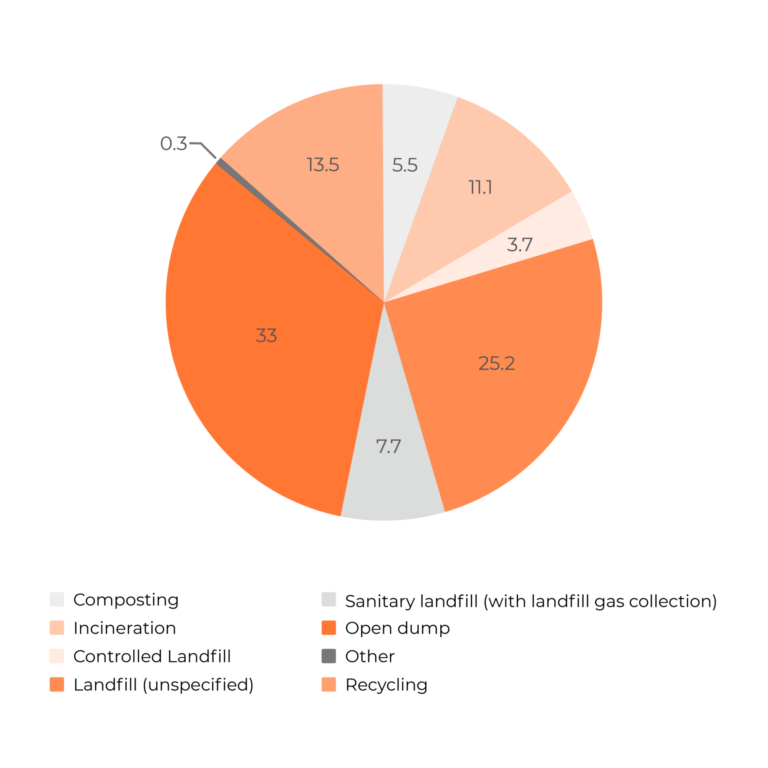
Global treatment and disposal of waste (percent)
For retail and hospitality businesses, AI-powered reverse vending machines are making an impact. These smart machines can identify and sort recyclable items like bottles and cans, offering rewards to encourage customer participation. It’s a win-win: businesses improve their recycling rates, while customers get incentives for being eco-friendly.
In offices and factories, AI systems are helping staff recycle more accurately. Smart bins with screens can show employees exactly what goes where, reducing contamination in recycling streams. Some systems even use gamification, turning proper recycling into a fun challenge for staff.
As these systems become more widespread, they’re set to transform how businesses approach waste, turning a necessary expense into a potential asset.
In manufacturing plants, smart cameras and sensors can quickly identify different types of metal alloys, plastics, and other materials on fast-moving conveyor belts. This precise sorting means more materials can be recycled, and fewer resources are wasted.
Construction and demolition sites are also benefiting from AI recycling solutions. Smart systems can analyze mixed debris, separating recyclable materials like concrete, wood, and metal from general waste. This reduces landfill use and cuts costs by recovering valuable materials that can be reused or sold.
In the mining industry, AI is helping to extract more value from waste rock and tailings. Advanced sorting systems can identify and separate tiny amounts of valuable minerals that might have been missed by traditional methods.
E-waste recycling facilities are using AI to tackle one of the fastest-growing waste streams. Smart robots can disassemble electronic devices, identifying and sorting different components for recycling. This process recovers precious metals and rare earth elements more efficiently, addressing a critical environmental and resource challenge.
The world of AI-powered recycling is evolving rapidly, with new technologies pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in waste management.
For example, the use of hyperspectral imaging in recycling plants. This technology can identify materials based on their unique spectral signatures, even when they’re not visible to the naked eye. This could be a game-changer for handling complex waste streams like electronic components or mixed plastics.
Another promising innovation is the integration of blockchain technology with AI recycling systems. This combination creates transparent, tamper-proof records of recycling processes. It allows companies and consumers to track materials from disposal through to their reuse in new products.
AI is also making waves in the field of chemical recycling. Smart systems are being developed to break down plastics into their chemical components, allowing them to be rebuilt into new, high-quality materials.
The impact of AI in recycling is far-reaching. As AI-powered solutions continue to evolve and become more widespread, we can expect to see significant improvements in recycling rates, reductions in landfill waste, and a decrease in the environmental impact of our consumption habits.
The future of recycling is smart, efficient, and increasingly automated – a future where AI helps us make the most of our resources and minimize our impact on the planet.


