In the previous article, we talked about mentorship skills as one of five skills that are important to the role of Technical Lead. This article will focus on leadership skills of the TL and how it should grow over time.
While technical expertise may earn respect, it’s leadership ability that truly transforms how teams function and deliver value. This article – the second in our five-part series on Technical Lead skills – explores the evolution of leadership capabilities across five developmental levels.
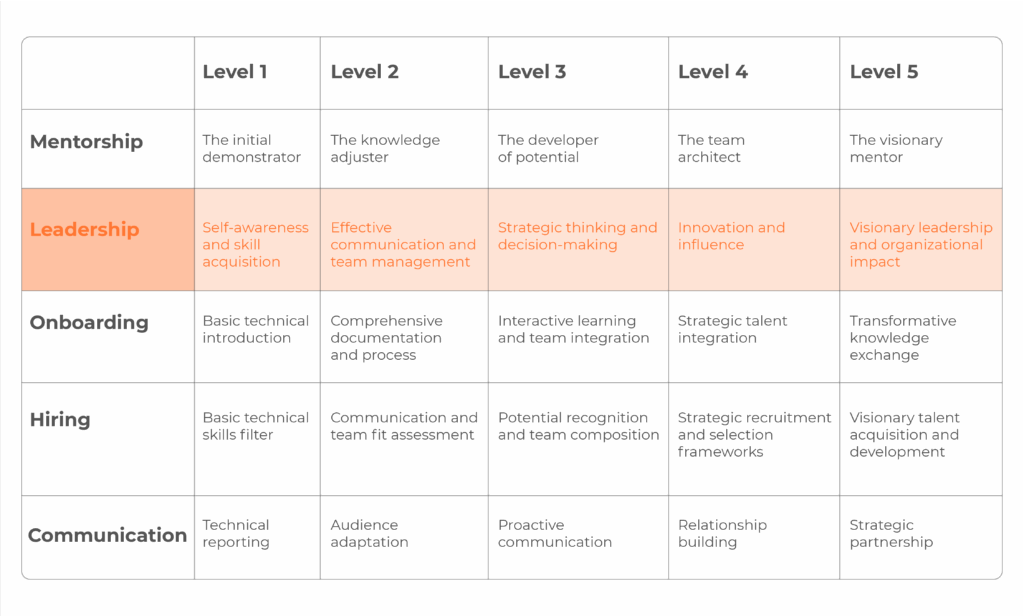
The evolution of leadership skills in technical leads
Level 1. Self-awareness and skill acquisition (junior)
Junior Technical Leads have strong technical foundations but are just beginning to understand their leadership style. They take initiative but may demonstrate impatience, rely heavily on others’ experience, and focus primarily on identifying and correcting shortcomings.
Advice for advancement:
Seek feedback on your leadership style from peers and mentors
Maintain a leadership journal documenting challenges and lessons learned
Practice active listening during team discussions before offering solutions
Study your team members’ working styles and preferences
Take a personality assessment (like MBTI or DiSC) to better understand your natural tendencies
Practice giving constructive feedback that balances critique with encouragement
Level 2. Effective communication and team management (middle)
Middle-level TLs communicate more effectively, manage team dynamics better, and can delegate tasks efficiently. They influence part of the team, plan responsibilities based on management input, and use group sessions more than individual coaching.
Advice for advancement:
Institute regular 1:1 meetings with each team member to complement group sessions
Create communication channels tailored to different types of information sharing
Develop a task allocation framework that considers both technical requirements and individual growth goals
Practice conflict resolution techniques before conflicts arise
Seek feedback on your delegation effectiveness from both team members and management
Identify and work with a leadership mentor who can provide guidance on difficult team situations
Level 3. Strategic thinking and decision-making (middle-high)
At this level, TLs engage in strategic thinking, plan for the team’s future, and make informed decisions that impact the broader organization. They help others take initiative, distribute responsibilities effectively, and maintain a general vision of their team’s direction within the company.
Advice for advancement:
Develop a quarterly strategic plan for your team that aligns with organizational goals
Create a team skills matrix to better allocate responsibilities based on strengths
Establish a feedback culture with structured processes for both positive and constructive feedback
Expand your network across the organization to understand interdepartmental dependencies
Develop presentation skills for effectively communicating your team’s value to upper management
Identify leadership opportunities beyond your immediate team responsibilities
Level 4. Innovation and influence (senior)
Senior TLs drive innovation within their teams, mentor others, and expand their influence across the organization. They facilitate cross-team collaboration, understand broader business contexts, and successfully resolve conflicts while maintaining team cohesion.
Advice for advancement:
Initiate cross-departmental projects that address organizational pain points
Develop and document best practices that can be adopted across teams
Create mentorship opportunities for up-and-coming technical leads
Build relationships with business stakeholders to better understand market needs
Establish innovation channels (hackathons, idea forums) where team members can propose improvements
Participate in industry events to bring external perspectives into the organization
Develop metrics to measure both technical and team health across multiple groups
Level 5. Visionary leadership and organizational impact (senior +)
At the highest level, TLs become visionary leaders who shape organizational culture, champion change, and have a significant, lasting impact on company success. They organize initiatives beyond their direction, articulate important company values, monitor engagement levels, and successfully resolve conflicts at any level.
Actionable advice:
Develop a personal leadership philosophy that inspires others
Create forums for discussing industry trends and their implications for the organization
Establish formal mentorship programs to develop the next generation of leaders
Build relationships with external partners to create strategic opportunities
Contribute to defining and refining organizational values and culture
Advocate for organizational changes that support long-term technical excellence
Participate in industry leadership activities to position your organization as a thought leader
The journey to visionary technical leadership
Leadership development represents a critical component of Technical Lead effectiveness. As TLs progress from self-awareness to visionary leadership, their impact expands from individual team performance to organizational direction and culture. The journey requires intentional development of both emotional intelligence and strategic thinking alongside continued technical growth.
Organizations play a crucial role in supporting this development journey through clear expectations, appropriate resources, and recognition systems that value leadership contributions. By understanding the characteristics and needs of TLs at each leadership level, companies can create targeted development opportunities that accelerate leadership growth.
In the next article in this series, we’ll explore the Technical Lead’s role in project onboarding – examining how TLs develop the capability to efficiently integrate new team members and clients into projects.
FAQ
What role does emotional intelligence play in the leadership development of a Technical Lead?
How can Technical Leads measure their progress in leadership development?
Progress can be measured through self-assessment tools, feedback from team members, and performance metrics related to project success and team satisfaction. Setting clear, achievable goals at each stage of leadership development and regularly reviewing these goals can help TLs gauge their improvement. Participation in leadership training programs and mentorship from experienced leaders can also provide benchmarks for measuring progress.
How can TLs foster a culture of innovation within their teams?
Technical Leads can encourage innovation by creating an environment where team members feel safe to express their ideas and take risks. This involves recognizing and rewarding creative efforts, facilitating brainstorming sessions, and providing resources for experimentation. Encouraging cross-disciplinary collaboration and staying open to adopting new technologies or methodologies can also spur innovation.
What strategies can TLs use to maintain team motivation and engagement at each leadership level?
How can TLs balance technical expertise with leadership responsibilities as they advance?
Chapters
- The evolution of leadership skills in technical leads
- Level 1. Self-awareness and skill acquisition
- Level 2. Effective communication and team management
- Level 3. Strategic thinking and decision-making
- Level 4. Innovation and influence
- Level 5. Visionary leadership and organizational impact
- The journey to visionary technical leadership
- FAQ



